调试技巧
✈️ 格式符
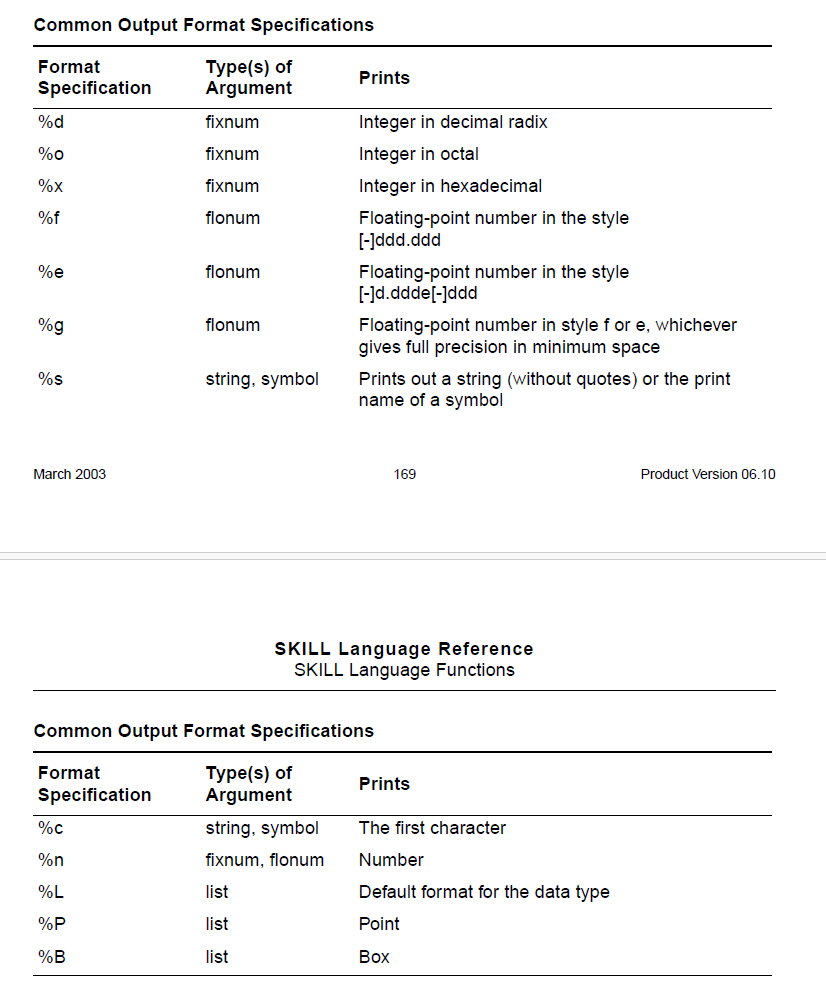
常用
- %d 十进制整数
- %f 浮点型
- %s 字符串或 symbol
- %c 单字符
- %n 数值
- %L list
- %P Point
- %B Bounding Box
🐹 整数类型格式符
| 格式符 | 参数类型 | 输出说明 |
|---|---|---|
%d | fixnum | 十进制整数 |
%o | fixnum | 八进制整数 |
%x | fixnum | 十六进制整数 |
🐹 浮点数类型格式符
| 格式符 | 参数类型 | 输出说明 |
|---|---|---|
%f | flonum | 浮点数以 [-]ddd.ddd 格式输出(如 123.456 或 -78.9) |
%e | flonum | 浮点数以科学计数法 [-]d.ddde[-]ddd 格式输出(如 1.234e+5 或 -6.78e-2) |
%g | flonum | 自动选择 %f 或 %e 格式,以最短宽度输出且保留全部精度 |
🐹 字符串/符号类型格式符
| 格式符 | 参数类型 | 输出说明 |
|---|---|---|
%s | string / symbol | 输出字符串(不带引号)或符号的打印名称(如符号 'abc 输出 abc) |
%c | string / symbol | 输出字符串或符号的第一个字符(如字符串 "hello" 输出 h) |
🐹 通用数字格式符
| 格式符 | 参数类型 | 输出说明 |
|---|---|---|
%n | fixnum / flonum | 输出数字(整数或浮点数,格式由类型决定) |
🐹 列表类型格式符
| 格式符 | 参数类型 | 输出说明 |
|---|---|---|
%L | list | 列表的默认格式输出(取决于数据类型) |
%P | list | 输出“点”(Point)格式的列表 |
%B | list | 输出“框”(Box)格式的列表 |
点击展开详情--官方原文说明
✈️ print 大法
按原有数据格式输出
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
p = outfile("D:/test.txt" "w")
width =12.5
netName ="XSIG123456"
print(width)
print(netName)
print(width,p)
print(netName,p)
close(p)
)执行效果如下 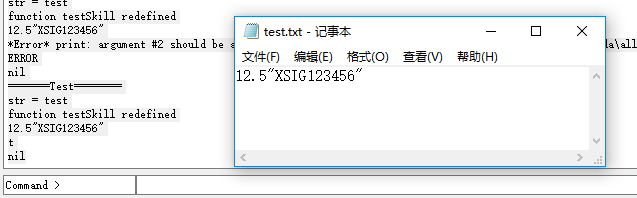
🐹 println
= print + newline()
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
p = outfile("D:/test.txt" "w")
width =12.5
netName ="XSIG123456"
println(width)
println(netName)
println(width,p)
println(netName,p)
close(p)
)执行效果如下 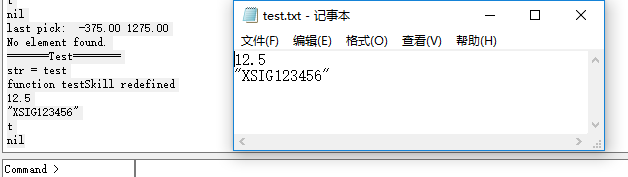
🐹 printf
格式化输出
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
width =12.5
netName ="XSIG123456"
printf("obj1=%f obj2=%s" width netName)
)执行效果如下
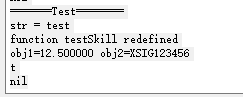
🐹 fprintf
带格式化输出到文件中
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
p = outfile("D:/test.txt" "w")
width =12.5
netName ="XSIG123456"
fprintf(p "%f --- %s" width,netName)
close(p)
)执行效果如下 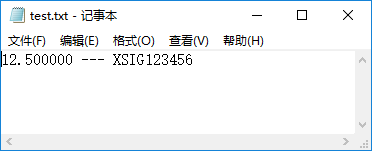
🐹 sprintf
格式化输出字符串[并赋值给变量(可选)]
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
width =12.5
netName ="XSIG123456"
;sprintf(nil "%f --- %s" width,netName)
sprintf(tmp "%f --- %s" width,netName)
printf("tmp=%s" tmp)
)执行结果如下 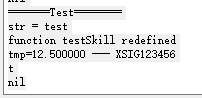
✈️ 弹窗
🐹 axlUIViewFileCreate
特别适用于脚本生成的文件,对应于 vbs 中的createobject("wscript.shell").run filepath
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
axlUIViewFileCreate("output.dat" "title" t)
)执行结果如下所示 
🐹 axlUIWPrint
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "Hello~")
)🐹 axlMsgPut
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
axlMsgPut("hello~")
)🐹 axlUIPrompt
带默认值的输入对话框
lisp
; 函数原型
axlUIPrompt("提示信息" "默认值" /password) => 字符串/nil功能:
- 弹出阻塞式对话框,强制用户响应后程序才继续执行
/password参数启用时输入内容会隐藏(如密码框)
场景:
- 获取用户输入的网络名:lisp
netName = axlUIPrompt("输入网络名称:" "GND") - 安全认证场景(隐藏输入):lisp
pwd = axlUIPrompt("输入管理员密码:" "" /password)
🐹 axlEnterString
lisp
; 函数原型
axlEnterString(?prompts '("提示语")) => 字符串/nil技巧:
- 通过
?prompts自定义输入框标题(如list("请输入坐标:")) - 用户取消时返回
nil,需做容错处理
场景:
lisp
layerName = axlEnterString(?prompts list("输入层名称:"))🐹 axlUIConfirm
lisp
; 函数原型
axlUIConfirm("警告信息" 'error) => t ; 始终返回t特性:
- 支持三级提示样式(参数:
'info/'warn/'error) - 受环境变量
noconfirm影响(若设置则直接返回)
场景:
- 执行危险操作前警告:lisp
axlUIConfirm("将删除所有未布线网络!" 'error)
✈️ 调试与延时
🐹 axldebug
函数语法
lisp
axlDebug(t/nil) => t/nil ; 返回上一次的调试状态启用调试模式
lisp
previousState = axlDebug(t) ; 开启调试,返回上一次状态
axlDebug(t) ; 开启调试
foreach(pin axlDBGetDesign()->pins
printf("Pin层: %s\n" pin->layer) ; 正确属性应为 'layerName'
) ; 立即报错提示 Invalid attribute 'layer'关闭调试模式
lisp
axlDebug(nil) ; 开启调试保存当前状态并开启调试
lisp
; 保存当前状态并开启调试
let((originalState)
originalState = axlDebug(t) ; 开启调试,保存原状态
; 执行需要调试的代码...
axlDebug(originalState) ; 恢复原始状态
)与 axlIsDebug 联动
lisp
; 仅当全局调试开启时才启用属性校验
if(axlIsDebug() then
axlDebug(t) ; 同步开启AXL调试
)🐹 axlIsDebug
lisp
; 函数原型
axlIsDebug() => t/nil ; 返回调试开关状态核心机制:
- 依赖环境变量
axldebug(开启时输出 API 参数错误详情) - 开发必开:捕捉函数调用错误(如传参类型错误)
使用建议:
lisp
when(axlIsDebug()
printf("DEBUG: 坐标类型错误!")
)🐹 axlSleep
lisp
; 函数原型
axlSleep(秒数) => t ; 固定返回t避坑指南:
- 替代 IPC 包的
sleep:避免 Windows 平台调用axlEnterEvent时崩溃 - 常用于异步操作等待(如等待渲染完成)
场景:
lisp
axlSleep(0.5) ; 暂停500毫秒等待画面刷新✈️ 错误机制
🐹 err
抛出异常中断
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
x = 0
when(x < 1
err('throw) ; 抛出异常并退出程序
)
(printf "x: %L\n" (x * 2)) ;
)执行结果如下 
🐹 error
格式化输出错误并中断
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
x = 0
when(x < 1
error("Error - X=%L\n" x) ; 抛出异常并退出程序
)
(printf "x: %L\n" (x * 2)) ;
)执行效果如下 
🐹 errset
可选是否抛出异常结束程序,或捕捉异常继续程序
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
; 此处执行可能触发异常的代码
; 手动触发异常
errset(
progn(
axlUIWPrint(nil "1")
axlUIWPrint(nil "2")
y=1/0
axlUIWPrint(nil "3")
)
t ;第2个参数默认是nil,设置nil和t发现都会打印错误信息,这是一个可选参数,可以不写
)
)核心机制:
| 执行状态 | errset 返回值 | errset.errset 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| 成功 | (结果值) | nil |
| 失败 | nil | (错误函数 错误码 标志 错误消息) |
示例:
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
x = 2
; 此处执行可能触发异常的代码
errset(y=1/1)
if( errset.errset then
(printf "errset.errset\n")
else
(printf "y: %L\n" y)
)
println(x * 2)
)执行结果如下

lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
x = 2
; 此处执行可能触发异常的代码
; 手动触发异常
errset(y=1/0)
if( errset.errset then
(printf "errset.errset\n")
else
(printf "y: %L\n" y)
)
println(x * 2)
)执行结果如下

lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
x = 2
; 此处执行可能触发异常的代码
; 手动触发异常
errset(
progn(
axlUIWPrint(nil "1")
axlUIWPrint(nil "2")
y=1/0
axlUIWPrint(nil "3")
)
)
if( errset.errset then
(printf "errset.errset\n")
else
(printf "y: %L\n" y)
)
println(x * 2)
)执行结果如下 
🐹 errsetstring
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
errsetstring("(1+2)")
)执行输入如下 
执行用户输入的公式计算,避免崩溃:
lisp
(defun testSkill ()
axlUIWPrint(nil "=======Test========")
let(
; 变量
(
(userInput "1/0")
)
; 执行表达式
progn(
if(result = errsetstring(userInput) then
printf("result = %L" car(result)) ; 提取结果
else
printf("error = %L" cadr(errset.errset)) ; 输出错误信息
)
)
)
)